
Dispatch from Digital Planet: June 2025
Dispatch from the Digital Planet is a monthly bulletin that talks about new updates in digital innovation across the world and their impact.

Dispatch from the Digital Planet is a monthly bulletin that talks about new updates in digital innovation across the world and their impact.

Dispatch from the Digital Planet is a monthly bulletin that talks about new updates in digital innovation across the world and their impact.

Dispatch from the Digital Planet is a monthly bulletin that talks about new updates in digital innovation across the world and their impact.

Dispatch from the Digital Planet is a monthly bulletin that talks about new updates in digital innovation across the world and their impact.

Dispatch from the Digital Planet is a monthly bulletin that talks about new updates in digital innovation across the world and their impact.

Dispatch from the Digital Planet is a monthly bulletin that talks about new updates in digital innovation across the world and their impact.

We studied the role of Systems Orchestrators in driving systemic changes on the ground to boost digital ecosystems and create jobs. We found that these orchestrators bring distinct advantages to transforming perceptions in the region.
In collaboration with Dalberg

Innovative businesses are key to sustainable development. This research highlights three companies: Husk Power Systems (sustainable energy), Nexsis (solar panels for essential services), and ThredUp (secondhand e-commerce). Insights emphasize the value of pay-as-you-go models, digital tech’s role in sustainability, women’s empowerment via regenerative tech, the need for government support in renewables, and maintaining consumer demand.
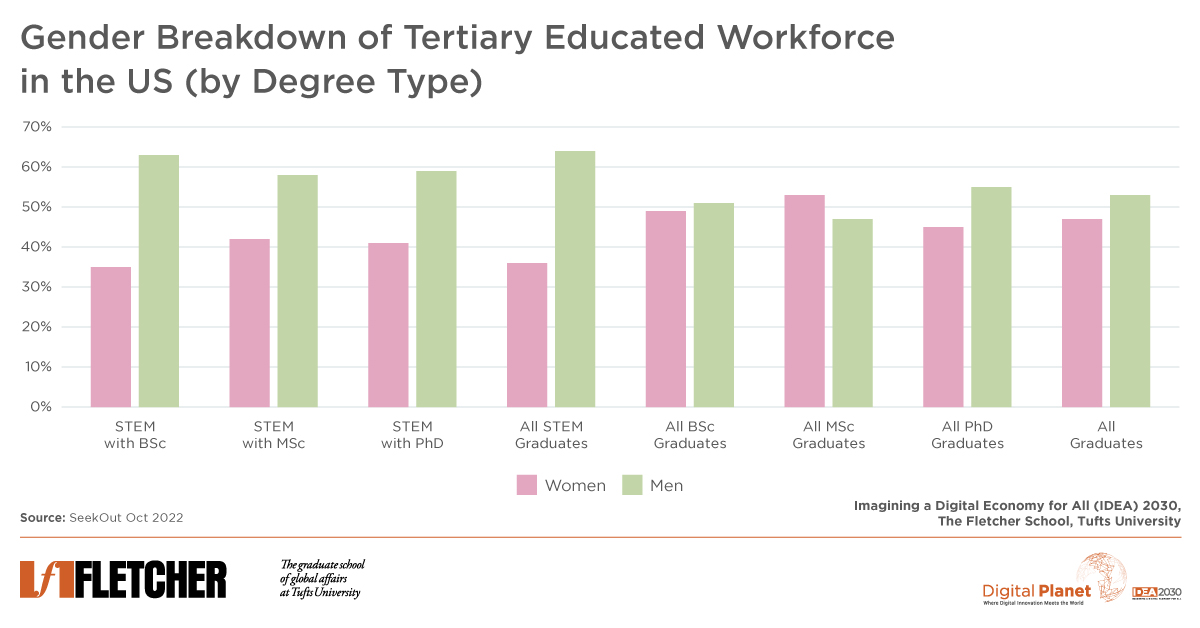
Women remain under-represented in high-paying technical and decision-making roles in STEM professions – a scenario that exposes the Achilles’ heel of the entire technology industry.

IDEA 2030’s report studies the link between digital inclusion and innovation. Key insight: As more join the digital economy, value creation focuses on affluent users, widening digital disparities. Policy interventions are needed for inclusive innovation.

Explore COVID-19’s effects on India’s digital economy, from lockdown challenges to the inclusion paradox. Discover strategies to bridge the gap and unleash India’s digital potential.

How can real-time social analytics provide a tool for inclusive policymaking? This report uses a dataset of over 873 million online interactions drawn from more than one hundred social and mainstream media channels to analyze public sentiment and emotion in response to the pandemic management of eight governments between January and July 2020.
In collaboration with Equiception

Recent global estimates suggest that school closures and unequal access to technology-based educational inputs used for remote learning will aggravate the existing equity gaps in education. ASER Digital Check 2020 captures information on various dimensions such as children’s sex, their school type, and their parents’ education level to explore this widening equity gap in education in rural India.
In collaboration with ASER Centre, Pratham India

Inclusive businesses use digital tech to advance global sustainability, worth $12-15T yearly. Studies highlight the need for trust, low-tech solutions, and environmental focus.

The under-representation of women in high-paying STEM roles is a vexing issue that exposes a systemic inertia across the industry.
Discover Ukraine’s Resilient Tech Economy Amidst Conflict. President Zelensky prioritizes economic preservation in the face of war, removing obstacles for SMEs. Tech sector fuels growth, accounting for $2B in Q1 2022. Learn how digital infrastructure, contingency plans, tax breaks, and security training contribute to its success. Follow our series ‘Imagining a Digital Economy for All in Ukraine’ to explore insights from industry leaders navigating the challenges. Adaptability, collaboration, and innovation redefine the future of work in a dynamic landscape.
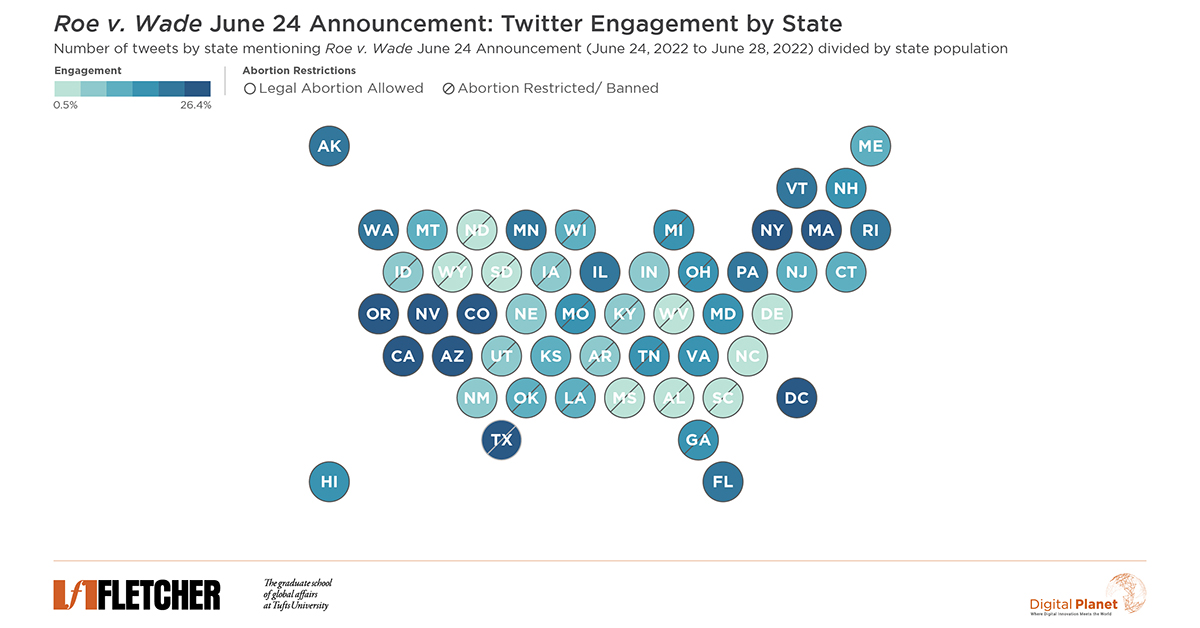
How did Twitter react to the Roe v. Wade announcement from the Supreme Court? What does this mean for abortion rights in America?
US broadband expansion lowered Covid mortality, especially in metro areas. Internet access is crucial in the public health toolbox.
The Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act allocates $65B to expand US broadband. We advocate a “people over miles” approach for equitable access.

We present Progress to Digital Parity—an interactive scorecard that tracks the journey towards realizing the goal of a digital economy for everyone, everywhere.

The needs of the global sustainable development agenda are both broad and urgent, and innovation models are central to addressing them in a timely, efficient, and scalable manner, from promoting inclusive growth and ensuring the longevity of natural resources to addressing issues across the state of the human condition.
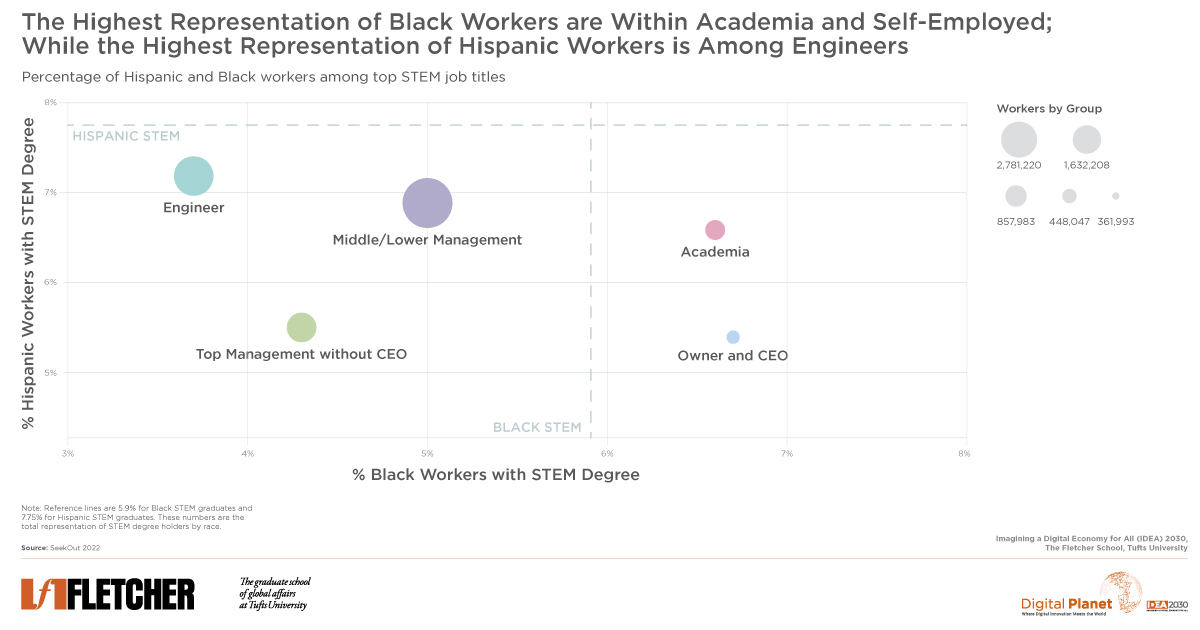
Despite strides in college attainment, Black Americans encounter obstacles in pursuing lucrative careers, especially in high-paying STEM roles within the technology sector.
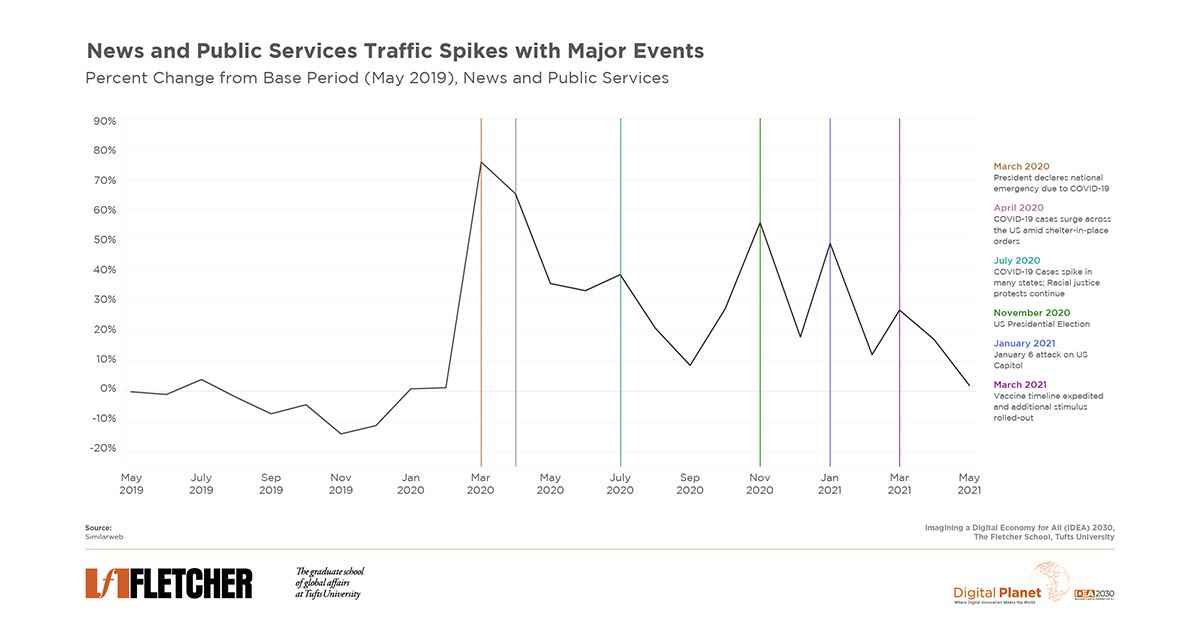
During the online shift, global digital adoption surged, advancing us digitally by 5 years in just 8 weeks.
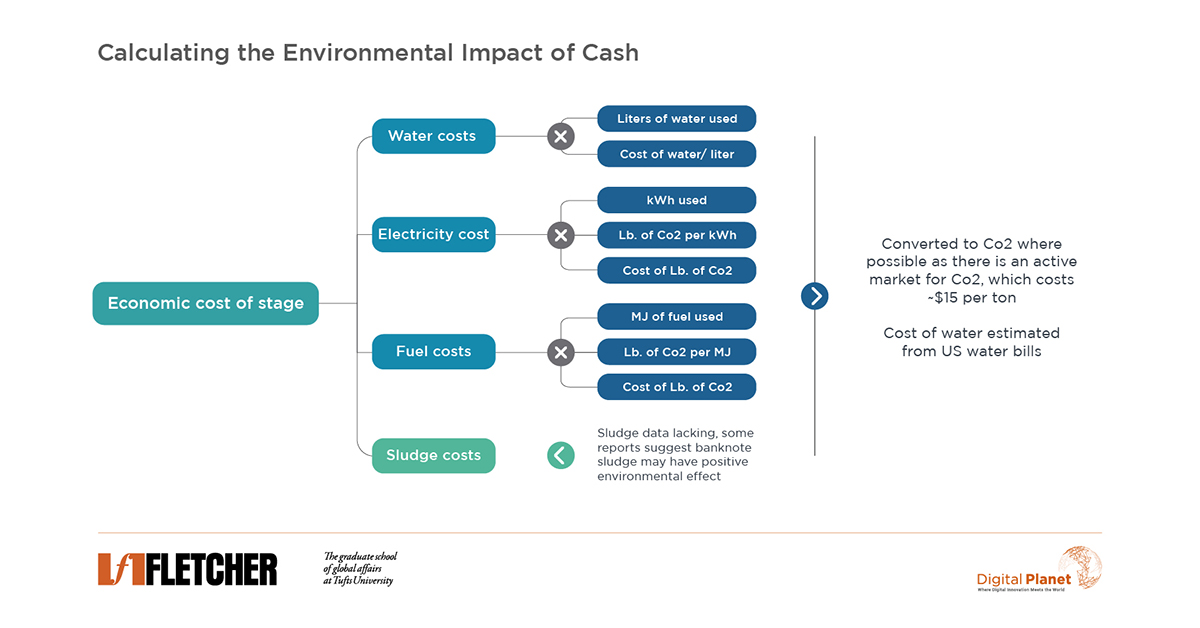
Value storage has costs: US cash notes at $0.26 each vs. Bitcoin’s $70 per coin CO2. Despite Bitcoin’s higher cost, cash notes’ total impact ($12.9B USD) far exceeds Bitcoin’s ($1.3B USD).
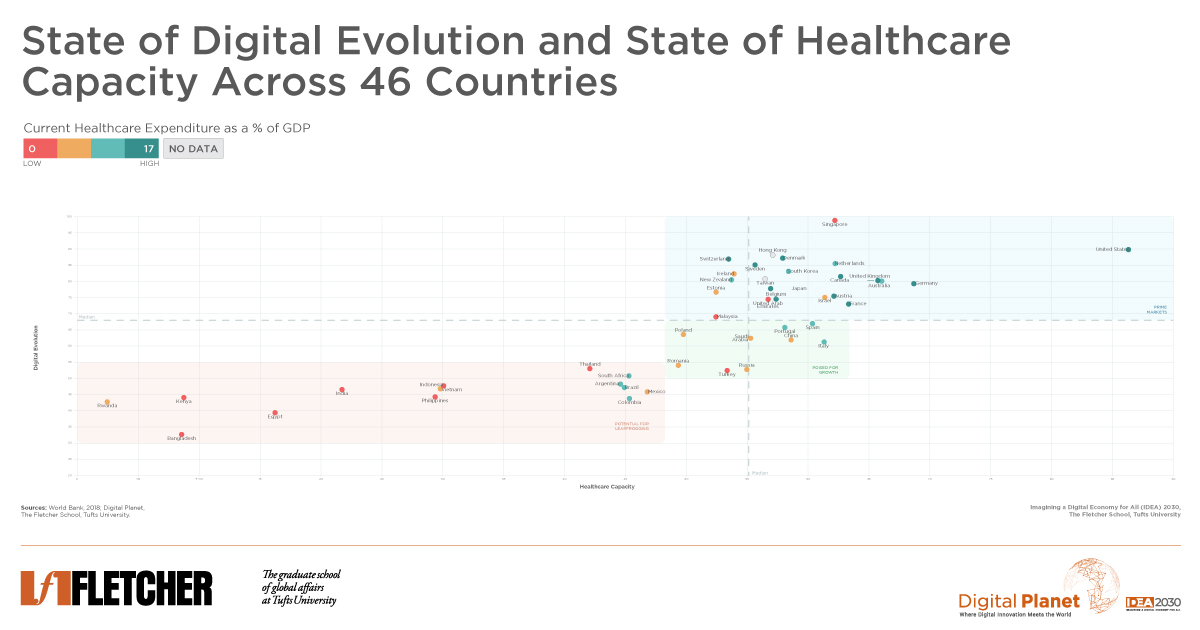
Global healthcare digitization varies wildly. Our study in 46 countries identifies virtualized healthcare opportunities, enabling lagging nations to leapfrog with digital tools for quality care.
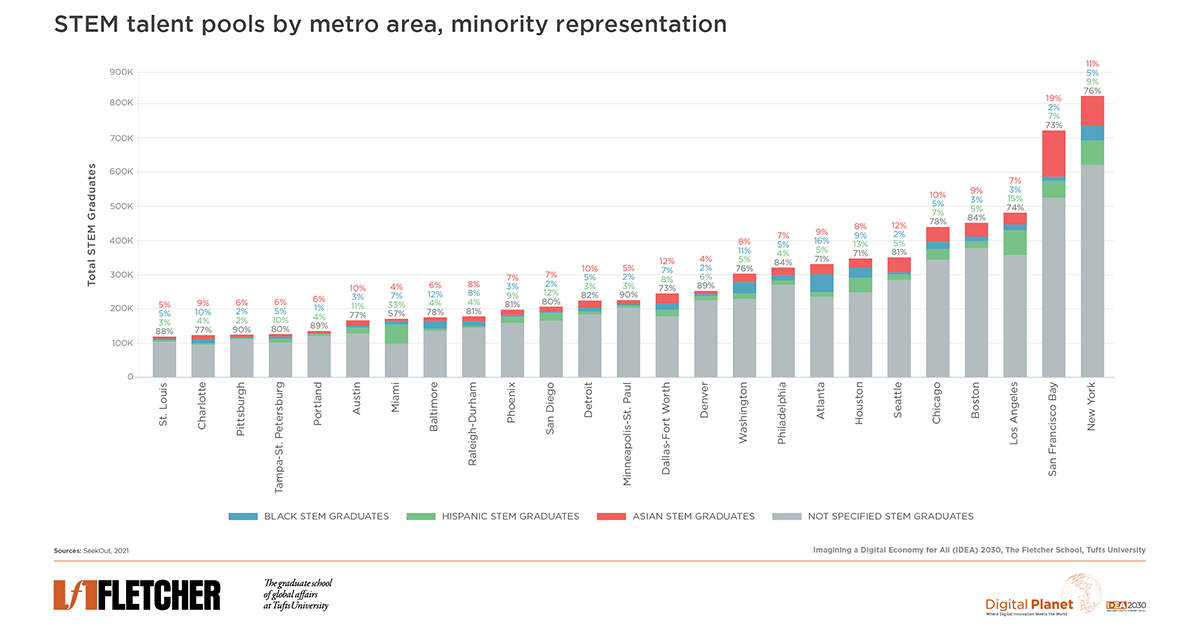
In the evolving work landscape, how can we boost under-represented talent (e.g., Black, Hispanic, female) in high-demand roles? Where can organizations find these diverse pools in major U.S. metro areas?

Why are we so divided about the true state of the digital divide in America? What steps might the Biden-Harris administration take to clarify the reality of this divide and move toward closing the gap? This webinar examines how these changes can be transformational for a recovering, yet socially distanced economy.
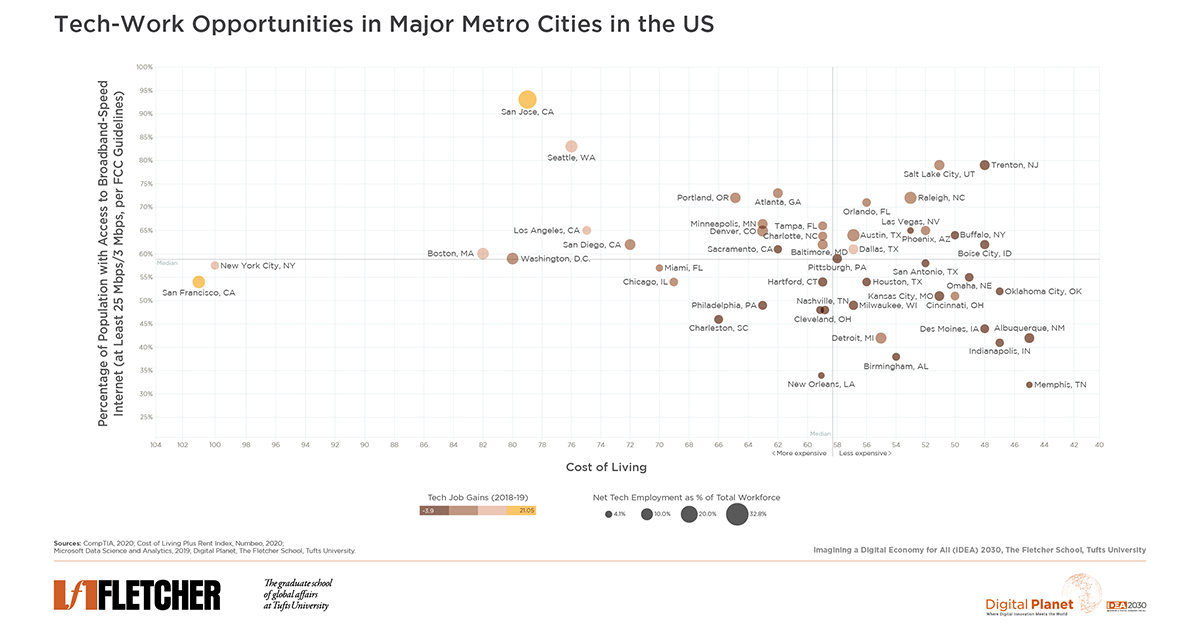
US States expanded telehealth, yet 16 of them face challenges with subpar broadband, hindering digital healthcare access.
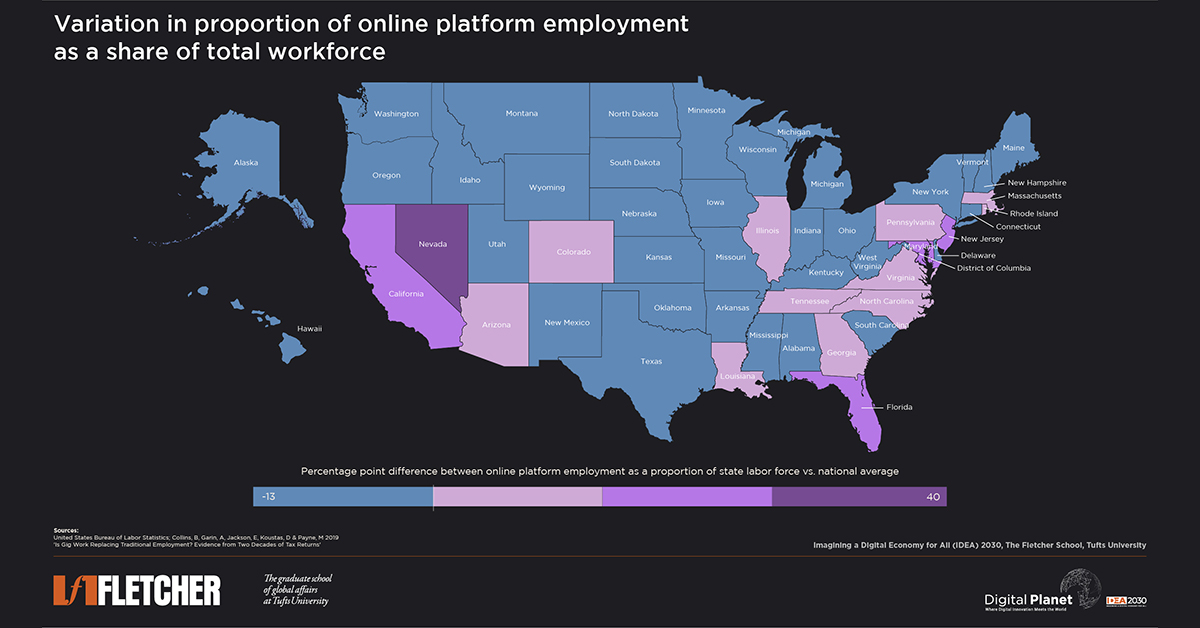
Digitally ready states thrived during the pandemic, leveraging gig workers for essential services. Yet, it revealed disparities and vulnerabilities in the gig economy.

An interactive research report that indexes trust in the digital economy and its evolution across 90 economies during the COVID-19 pandemic. This report features a collaborative research platform that provides data and evidence-driven actionable insights to leaders in government, business and technology.
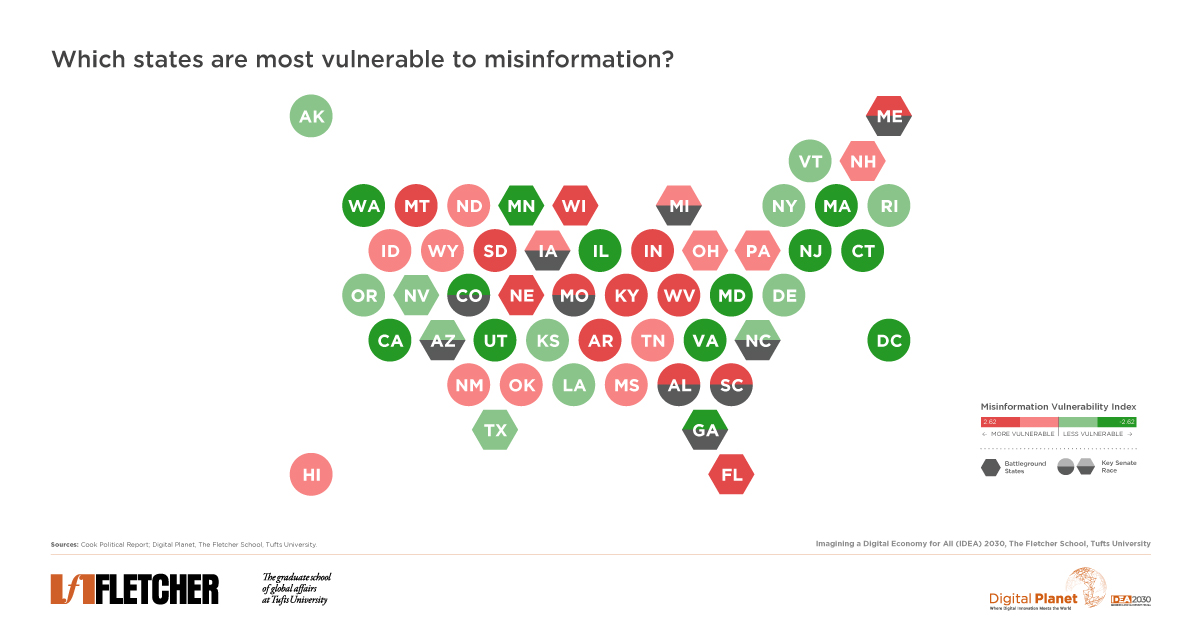
US parties race, relying on digital platforms. Public dependence on social media for news raises concerns about misinformation amid the COVID-19 pandemic, fueling a surge in digital crime.
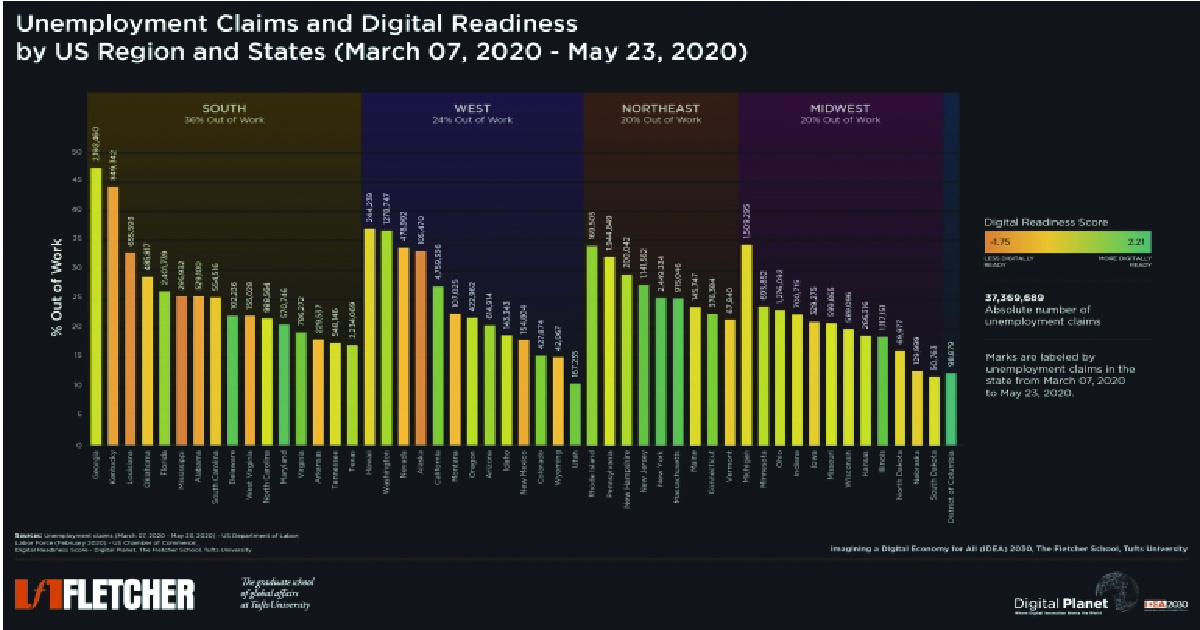
Digital platforms are crucial for business continuity during COVID-19. Washington excels in remote work, job transitions, and online unemployment filing support.
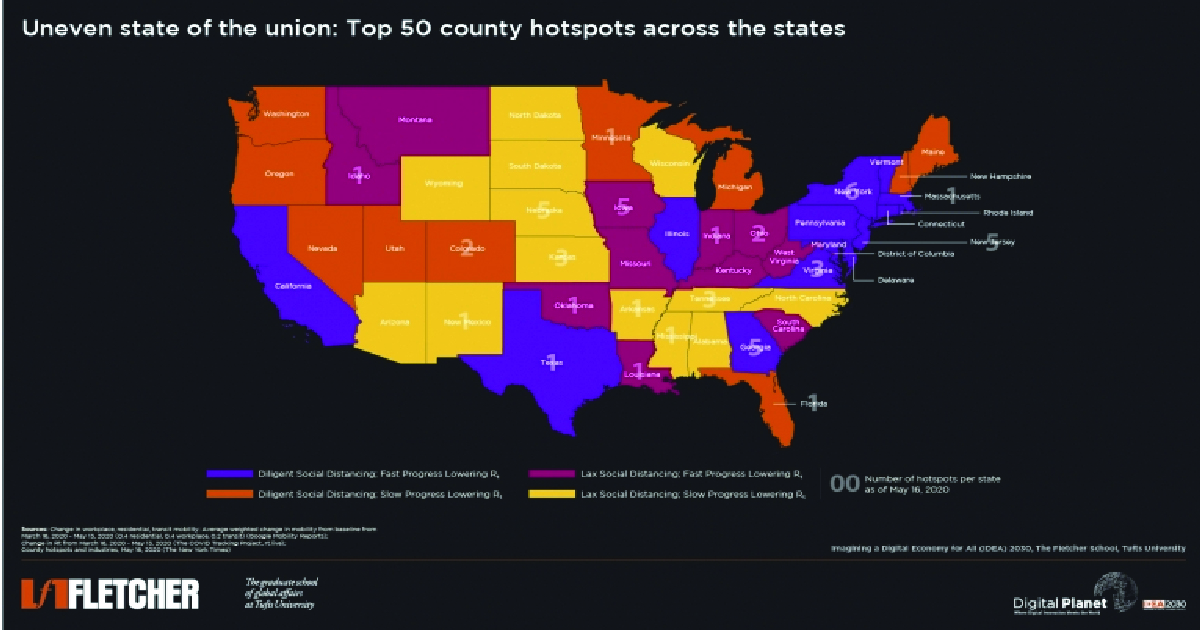
Despite 1.67M cases and nearly 100K deaths, US states vary in easing COVID-19 restrictions due to a lack of federal guidance.
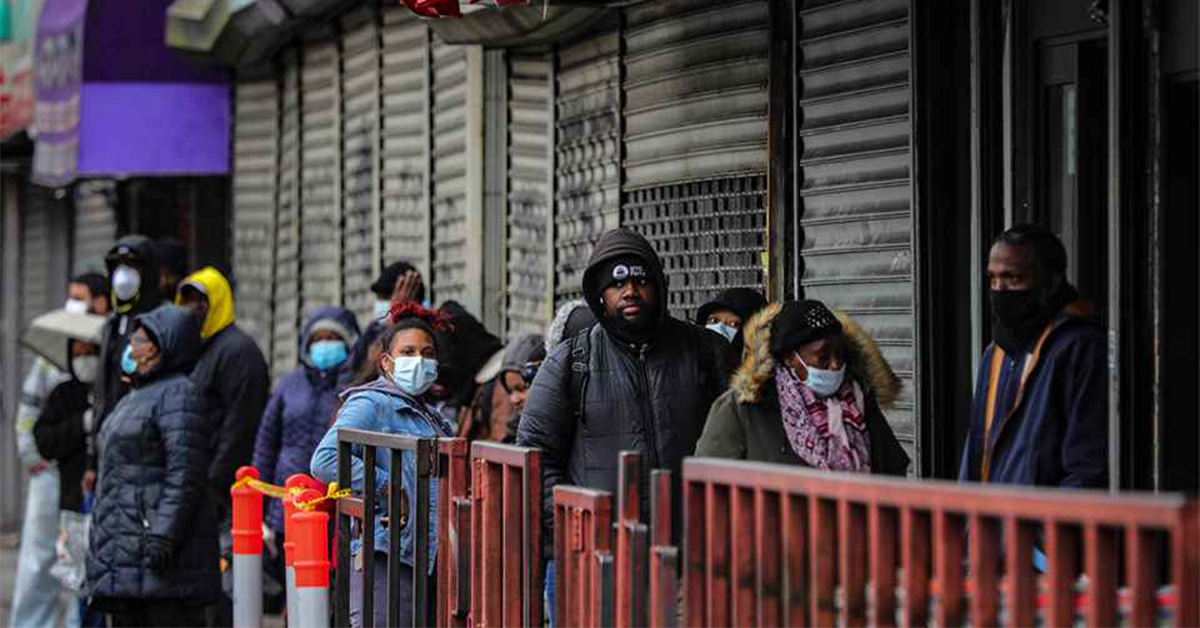

COVID-19 reveals US inequality, with races over-represented in inflexible, low-tech jobs due to limited internet access.
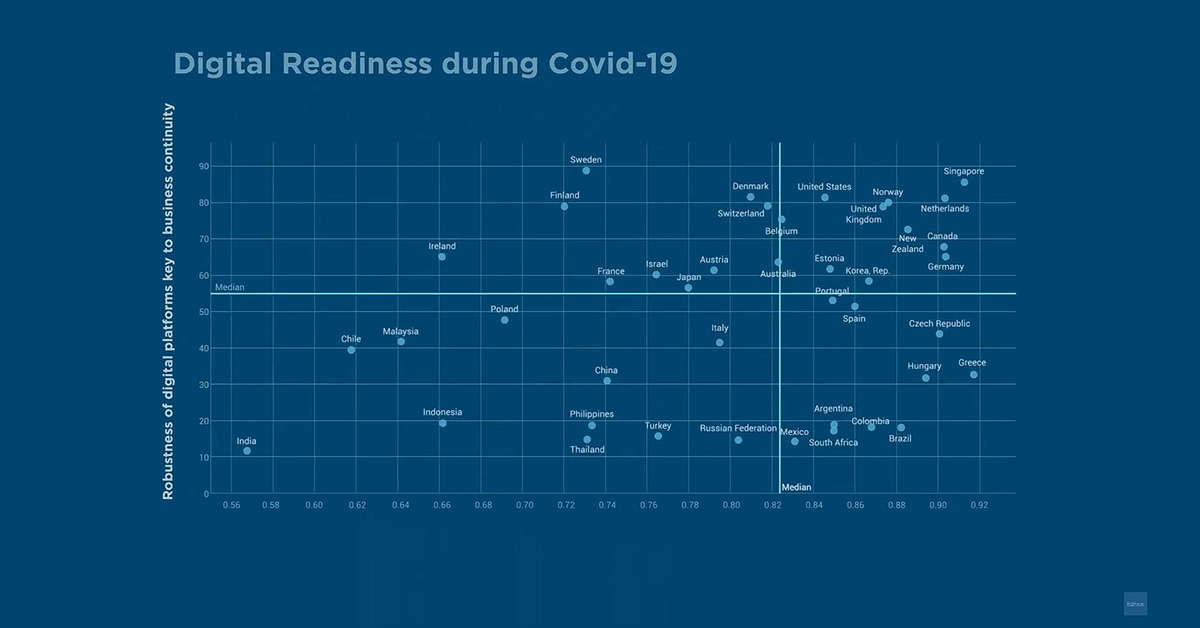
Are countries around the world prepared to keep the wheels of their economies turning during Coronavirus lockdowns? Watch the Social Distance Readiness Benchmark video summary to find out.
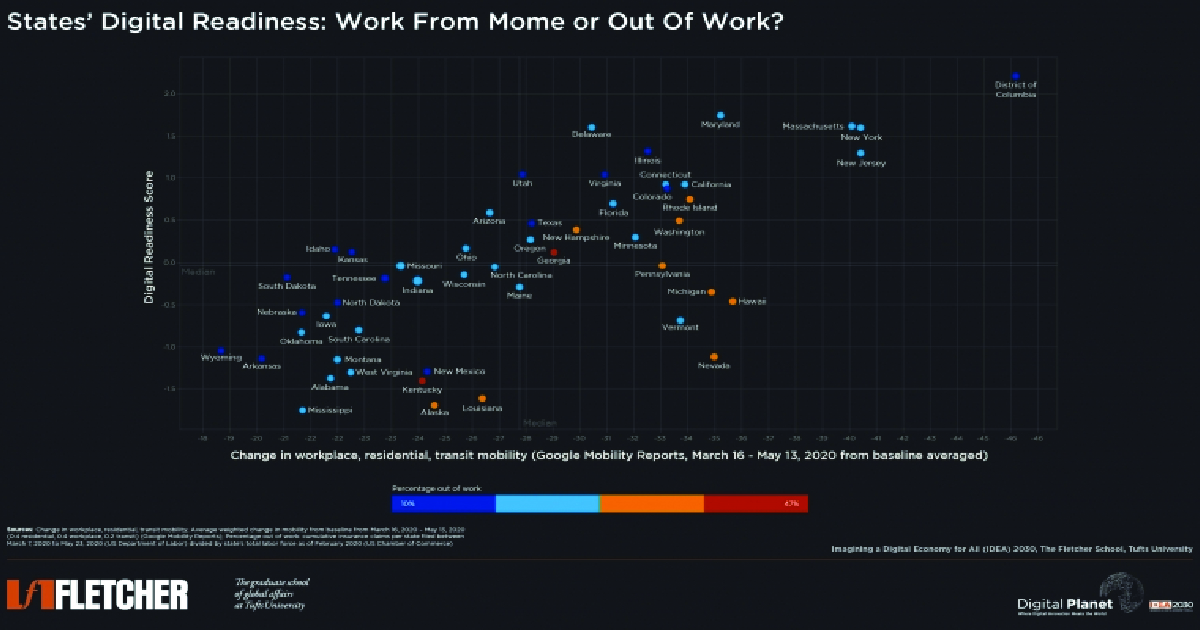
During the COVID-19 lockdown, US States that were least digitally ready and had the strictest social distancing measures experienced the highest unemployment numbers.
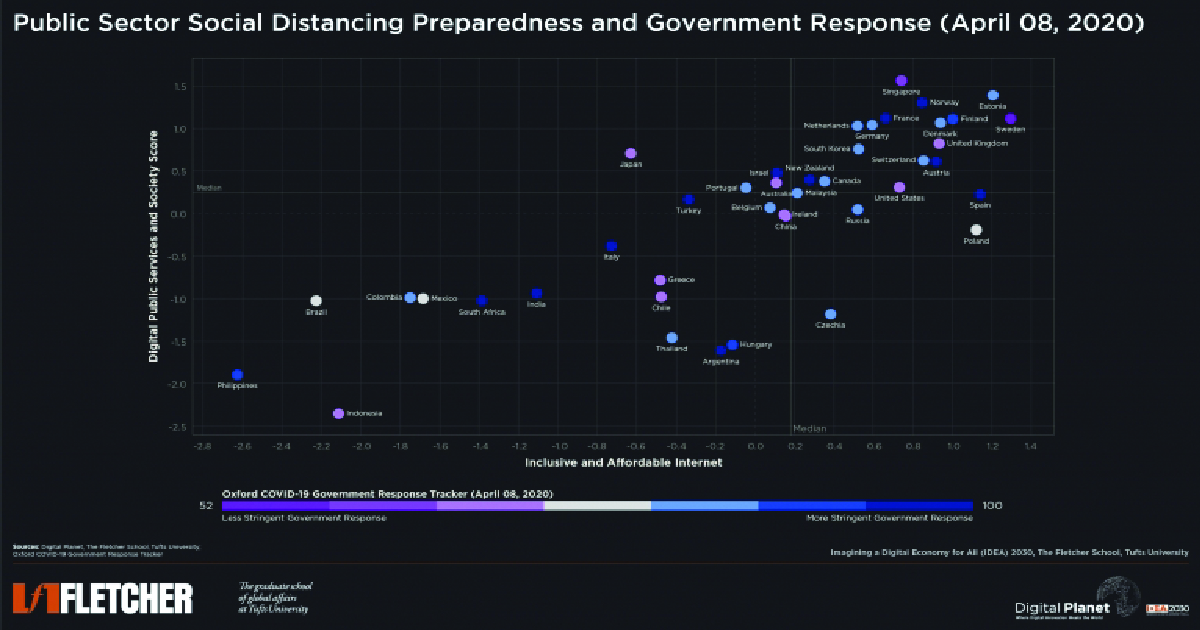
Online public services need infrastructure and affordable internet. We scored 42 countries on digital services and internet access, considering lockdown measures.

Watch the video summary to learn more about the key takeaways from the African Leapfrog Index.

Online public services need infrastructure and affordable internet. We scored 42 countries on digital services and internet access, considering lockdown measures.
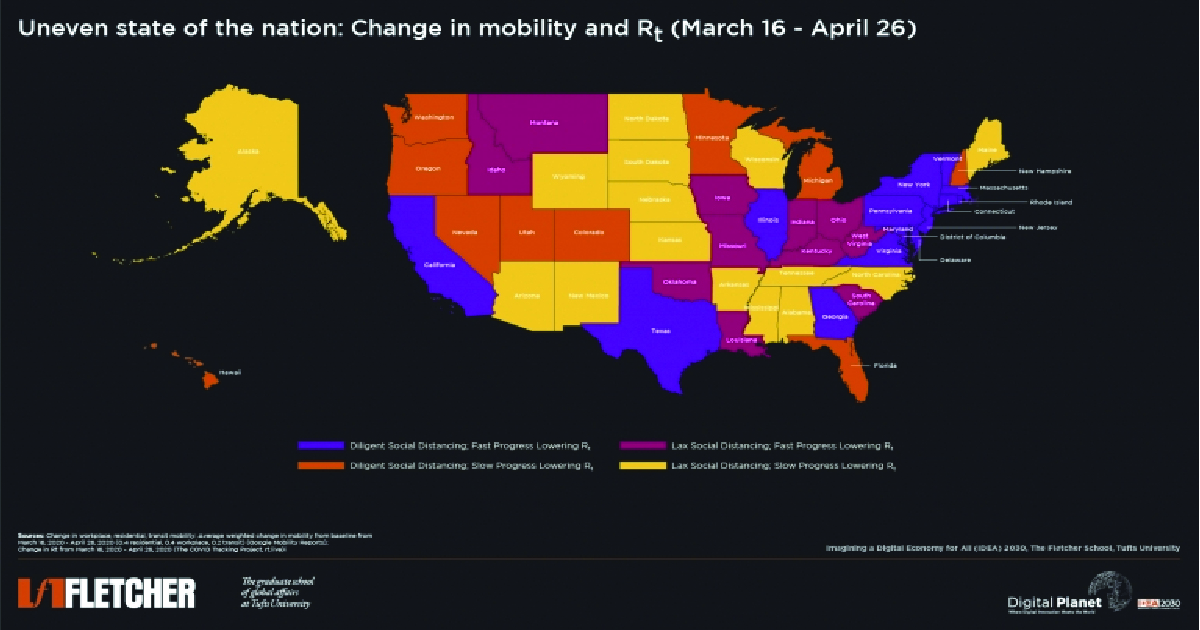
How does COVID-19 affect various US regions? Digital Planet analyzed mobility changes in relation to the virus reproduction rate.
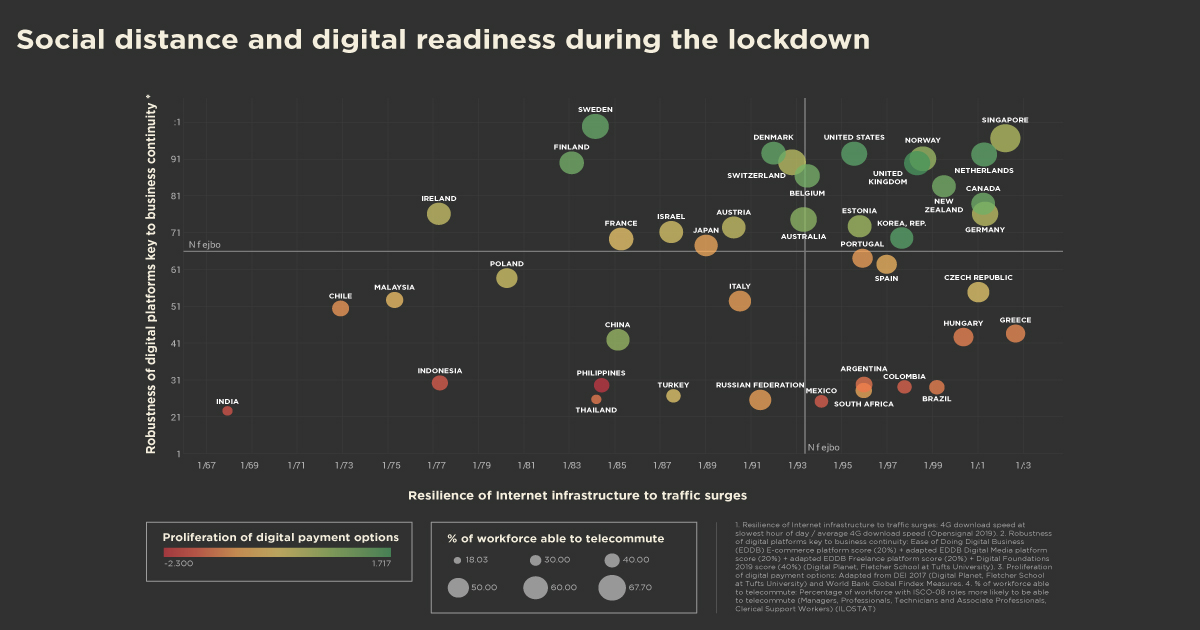
Remote work depends on digital services – telecom, e-commerce, digital media for communication. Countries need robust digital payments for transaction surges.

How emerging technologies and digital transformations can accelerate economic and societal growth in 6 African countries.

A Social Distance Readiness analysis of 42 countries measuring the robustness of their digital platforms; resilience of internet infrastructure to traffic surges; proliferation of digital payments options and percentage of workforce able to telecommute.

The African Leapfrog Index (ALI) is a novel framework that draws upon the primary levers that facilitate the translation of digital technologies into development and inclusive growth. The framework evaluates six African countries against a continent-wide “best-performance” benchmark to identify strengths to build upon and the opportunities to close gaps.

The Digital Evolution Index: Latin America and Caribbean Edition (DEI LAC) is a data-driven study of the pace of digital growth in 24 LAC countries across four key drivers of supply, demand, institutional environment, and innovation. It utilizes 99 unique indicators measured over a ten-year period (2008 – 2017) to create an overall digital evolution score and digital momentum score.

If the yardstick of effectiveness of any scorecard or ranking were tangible efforts, by those graded, to “improve bad ratings or maintain good ones,” few come even remotely close to the World Bank’s annual Doing Business survey.

Which countries help expedite entry, growth, and exit of technology-based businesses?

The Digital Evolution Index 2017 is a data-driven holistic evaluation of the progress of the digital economy across 60 countries, combining more than 100 different indicators across four key drivers: Supply Conditions, Demand Conditions, Institutional Environment, and Innovation and Change. The resulting framework captures both the state and rate of digital evolution and identifies implications for investment, innovation, and policy priorities.

The Cost of Cash: Mexico report does more than simply estimate how much time and money Mexican consumers invest in access to cash. It also asks what groups in society are most likely to pay for access to cash with fees, transit times, and queue times; rich or poor, young or old, Northern or Southern, male or female, and rural or urban. It asks whether financial traits are equally important.

India’s economic growth propels financial revolution via modern services. Cash-heavy economy, low non-cash payments, high cash management costs analyzed. Technology, Aadhaar key for cash-to-digital shift. RBI, banks face currency operation costs. Report stresses payments’ role in inclusion, cash reduction benefits.

Explore the enduring relevance of cash in today’s digital world. Discover the reasons behind its persistence, including anonymity, control, and trust. Learn about the challenges faced by digital alternatives and the complex interplay of habits, regulations, and technology in the cashless revolution. Dive into a comprehensive study shedding light on the costs and benefits of cash use across various stakeholders in the American economy.